3D Graphics Programming with QuickDraw 3D 1.5.4
Previous | QD3D Book | Overview | Chapter Contents | Next |
Tori
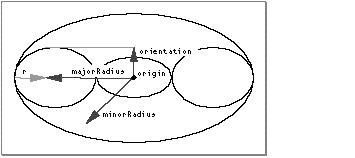
Figure 20 shows a torus.
Data Format
Vector3D orientation
Vector3D majorRadius
Vector3D minorRadius
Point3D origin
Float32 ratio
Float32 uMin
Float32 uMax
Float32 vMin
Float32 vMax
- orientation
- The orientation of the torus. This field specifies the axis of rotation and half-thickness of the torus. The orientation must be orthogonal to both the major and minor radii.
- majorRadius
- The major radius of the torus.
- minorRadius
- The minor radius of the torus.
- origin
- The center of the torus.
- ratio
- The ratio of the length of the major radius of the rotated ellipse to the length of the orientation vector of the torus. (In Figure 20 , this is r length( orientation .) This field indicates the eccentricity of a vertical cross-section through the torus (wide if ratio > 1, narrow if ratio < 1).
- uMin
- Minimum parametric limit value for u. To understand u, first consider u for the ellipse determined by majorRadius and minorRadius . If the torus is thought of as a doughnut, one can think of the doughnut as created by starting with this ellipse and making it thicker. The value of u on this ellipse is parametrized by the angle between the major axis and the vector from the origin to the circumference of the ellipse. The value u = 0 corresponds to 0 radians, and u = 1 corresponds to 2 radians. The values uMin and uMax are used to create partial ellipses. The basic idea is that only the part of the ellipse between uMin and uMax is drawn. For such a partial ellipse, the partial torus can be thought of as the part of the doughnut between uMin and uMax . For details, see the QD3D documentation or develop magazine, Dec. 96. Must be 0 in Version 1.5.
- uMax
- Maximum parametric limit value in u direction; see uMin above. Must be 1 in Version 1.5.
- vMin
- Minimum parametric limit value in v direction. To understand v, we start with the ellipse described above for the uMin field. Pick any point p on this ellipse, and consider the following second ellipse: One axis is the orientation vecto r rooted at point p . The other axis (call it M ) has the same direction as a vector from point p to the torus' origin, and its length is (ratio) times (length of orientation vector). This second ellipse describes the profile of the tube of the doughnut. The parametric value v of a point q on this ellipse is given by the angle between axis M and a vector from point p to point q . The value v = 0 corresponds to 0 radians, and v = 1 corresponds to 2 radians. The values vMin and vMax are used to create partial ellipses. The basic idea is that only the part of the ellipse between vMin and vMax is drawn. Assuming that uMin = 0 and uMax = 1, if vMin != 0 and vMax != 0, the resulting partial torus can be thought of as a whole doughnut with a wedge-shaped groove cut out of it. For example, if uMin = 0 and uMax = .5, the result looks like a bagel sliced in half, ready to have cream cheese spread on it. The value of vMin must be 0 in Version 1.5.
- vMax
- Maximum parametric limit value in v direction; see vMin above. Must be 1 in Version 1.5.
Description
A torus is a three-dinensional object formed by the rotation of an ellipse about an axis in the plane of the ellipse that does not cut the ellipse. The major and minor radii of the torus are the distance of the center of the ellipse from that axis.
Default Surface Parameterization
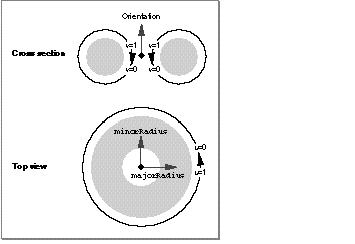
The default surface parameterization for a torus is as shown in Figure 21 .
Figure 21 The defalt surface parameterization of a torus
Examples
Container (
Torus (
0 .2 0 #orientation
1 0 0 #majorRadius
0 0 1 #minorRadius
0 0 0 #origin
.5 #ratio
0 #uMin
1 #uMax
0 #vMin
1 #vMax
)
Container (
AttributeSet ( )
DiffuseColor (1 1 0)
)
)
© 1997 Apple Computer, Inc.
Previous | QD3D Book | Overview | Chapter Contents | Next |